Characteristics/Features of Private Limited Company
November 19, 2025 by Team Instabizfilings
What is a private limited company?
In India the private limited company stands as one of the country's most popular business entities because it represents an incorporated entity that has limited liability functions. Indian companies favor the private limited business entity because of its protection, formation ease and standalone legal identity aspects. The potential entrepreneurship program stimulates individuals to establish their business ventures. Private limited companies must serve at least two members and directors yet maintain full legal independence from proprietors to operate. Private limited companies in India operate under the following distinct characteristics:
-
Limited Liability Protection: The shareholders of a private company enjoy the protections of their limits to liability that are legally limited to the same. The shareholders of the company guard the business assets of the company irrespective of the financial hardships experienced by the company.
-
Separate Legal Entity: A private company operates with legal independence apart from its owners. Under its own unique legal identity a private limited company can own properties, conduct contracts and fight or support court proceedings.
-
Minimum Number of Shareholders: A private enterprise needs minimum two shareholders and it has strict limits of 200 shareholders.
-
Minimum Number of Directors: A business requires at least two directors so as to qualify as limited company. At least one of the directors of the limited company must be an Indian citizen.
-
Minimum Share Capital: It is no longer necessary to have a minimum share capital - of Rs. 1,00,000/-
-
Name of the Firm: A private limited company must add "Private Limited" as the last part of its business name.
-
Restrictions on Share Transfer: Share ownership within a private limited company faces restrictive barriers to transfer. Shareholders need Board of Director approval and can complete transfers based on the company's Article of Association.
-
Prohibition on Public Invitation: Private limited companies cannot invite public subscriptions to their share or debenture offerings.
-
Compliance Requirements: Private limited companies must fulfill several legal obligations through requirements to maintain complete financial records while conducting annual general meetings and filing annual reports at the ROC.
Various attributes that accompany registration of Private limited companies in India make it the preferred company type used by entrepreneurs due to the ease with which the business is run in addition to a conducive setting the process offers.
Types of Private Limited Companies
Business owners considering startup company formation need to study the private limited company.
-
Company Limited by Shares: Shareholders of private limited companies have specific financial responsibility because they only need to contribute the stated share price from their Memorandum of Association.
-
Company Limited by Guarantee: Company regulations state that members bear financial responsibility for company debts up to the value of their obligation's specified guarantee. Shareholders only assure that they would get paid when a company is being wound up.
-
Unlimited Companies: Members of unlimited companies must bear unlimited personal responsibility when their company becomes indebted or incurs liabilities. Yet these entities retain their sovereign corporate status which shields directors from personal legal action.
Company Registration Process
The company registration process in India follows a simple four-step system which users can easily complete:
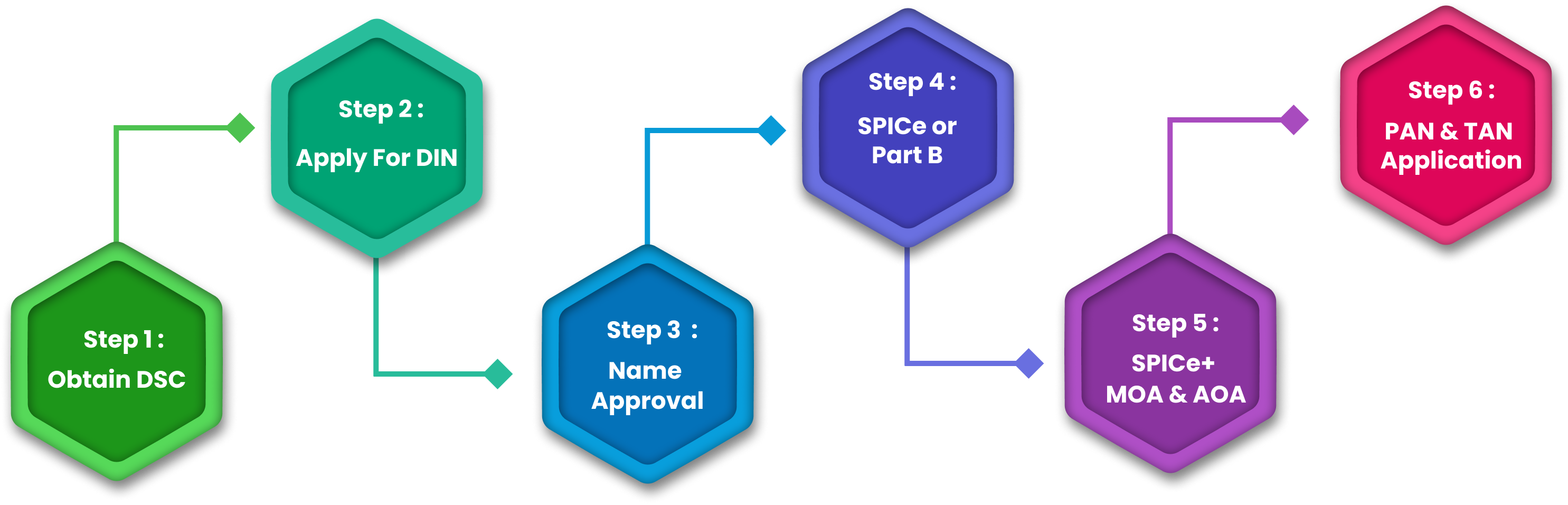
Step 1: A company which intends to operate should have Digital Signature Certificate (DSC)
-
The directors, shareholders who run the business of the companies are compelled to purchase the Digital Signature Certificates (DSC) with the Controller of Certification Agencies (CCA). Fundamental registration information must be supplied to the authorities which includes passport photos and your PAN details together with Aadhar Card information and phone number and email address. Foreign nationals need to provide both notarized and legally stamped documents for the application process.
Step 2: Director Identification Number (DIN)
-
Before taking up the role of company director you must obtain a Director Identification Number (DIN). The process of registration obliges all directors to obtain and enter a DIN.
Step 3 The Company (SPICe+ Part A) Application Functions as a Name Reservation system
-
The company's distinct name needs to be secured through the SPICe+ Part A document system. To register the company users must select the business format and classification followed by picking the appropriate categories and subclasses while declaring the key industrial operation. Two potential names require your submission for approval during the application process.
Step 4: The SPICe+ Part B form requires submission of all the information about the company
-
Company registration in India requires users to supply full details regarding capital structures and stamp duty payments as well as PAN and TAN applications together with necessary supporting documentation and subscriber and director information and chosen office address.
Step 5: Companies must create and submit two documents containing company specifications to the MCA through SPICe+ MOA and AOA
-
Create the essential company details in draft format for your MOA along with AOA. The MCA needs signed digital documents from subscribers along with professionals before they can approve these submissions.
-
Business members need to file the AGILE-PRO-S form to initialize their registration for GST and EPFO and ESIC as well as establishing a bank account while getting a shop and establishment license depending on state regulations.
-
Successful businesses will be given Certificate of Incorporation (COI) having Company Identification Number (CIN), PAN and TAN by the MCA.
You must complete these standard procedures to establish a company successfully within India.
All You Need to Know About Advantages and Disadvantages of LLP
Private Limited Company registration fees & cost
Fees breakup for Private Limited Company registration (example up to ₹1,00,000 authorised capital)
| Cost component | Amount (₹) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Professional fees – Starter Package | 8,999 | Includes name approval, DSC (2), DIN (2), MOA, AOA, incorporation, PAN, TAN. |
| Estimated government fees (MCA, ROC) | 2,500 | For basic authorised capital of ₹1,00,000 (varies by state & capital). |
| GST registration (if opted) | 0 | Complimentary in Growth Package. |
| MSME registration (if opted) | 0 | Complimentary in Growth Package. |
| Trademark application (if opted) | Professional: 0, Govt: as per class & entity | Professional fee covered in One Stop Package; govt fees extra at actuals. |
Final pricing may vary depending on your authorised capital, state of registration and any additional registrations or add‑on services selected.
Read More: This paper aims at discussing the process of converting a public limited company to a private limited company.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this blog is purely for general informational purposes only. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy, reliability and completeness of the content presented, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, for the same.
We expressly disclaim any and all liability for any loss, damage or injury arising from or in connection with the use of or reliance on this information. This includes, but is not limited to, any direct, indirect, incidental, consequential or punitive damage.
Further, we reserve the right to make changes to the content at any time without prior notice. For specific advice tailored to your situation, we request you to get in touch with us.

Need more details? We can help! Talk to our experts now!
Start Your Business Registration – Talk to Our Experts Now!

Still Confused?
Talk to experts? Fill in the information and we will reach out in 24 Working Hours.

